By Kevin Gao
On August 12, 2017, EqOpTech hosts a sixth tech talk in a series of Speaker/Workshop for students interested in the tech fields. The tech talk features Scott Best, technical director of anti-counterfeiting in the Rambus Cryptography Research Division.
Scott Best, Technical Director, Rambus Crytography Research Division
**What is Gold?**
Best leads off the meeting by introducing gold: why is it so special? From all the elements on our periodic table, why does gold hold such an important role?
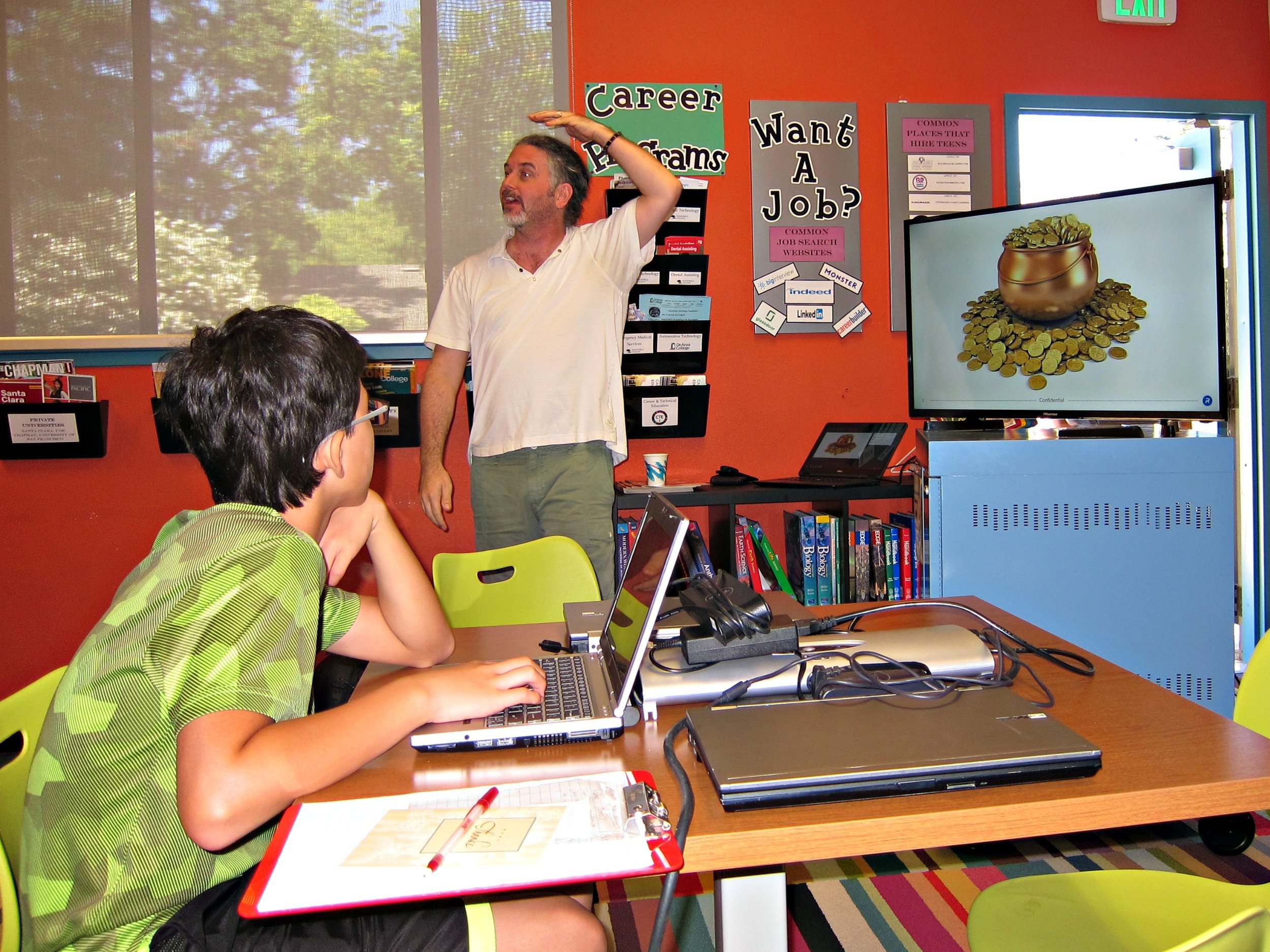
We all know that gold is a rare and precious metal, but where exactly does it come from? When a star explodes (going supernova!), it scatters precious metals all across the universe. In the form of meteorites, many of these metals landed on our planets hundreds of millions of years ago. Among these were many of our well-known metals today, including nickel, copper, platinum, and of course, gold.
**Money**
Money is something that has been around since early civilization, going all the way back to when Aristotle postulated that a good form of money must be durable, portable, divisible, and have an independent value. For centuries, people have used it as a quick, easy way to exchange goods and to be able to repay a debt without having to bring items of similar values. In his talk, Best describes money as “a matter of functions four: a medium, a measure, a standard, a store”. In other words, for something to be money, it must satisfy the following requirements:
- Medium: can buy stuff with it?
- Measure: how valuable is that thing?
- Standard: how much do you owe me?
- Store: piggy bank
Two types of money that fits these requirements are our currency and credit cards, both of which we see very often in our daily lives. Before these were created, another type of money used was in the form of gold. Best describes that while other metals may be too abundant or dangerous to serve as a form of money, gold is finite and valuable, fitting the requirements above perfectly. Finally, another form of money has recently come into existence: the bitcoin.
**Security!!**
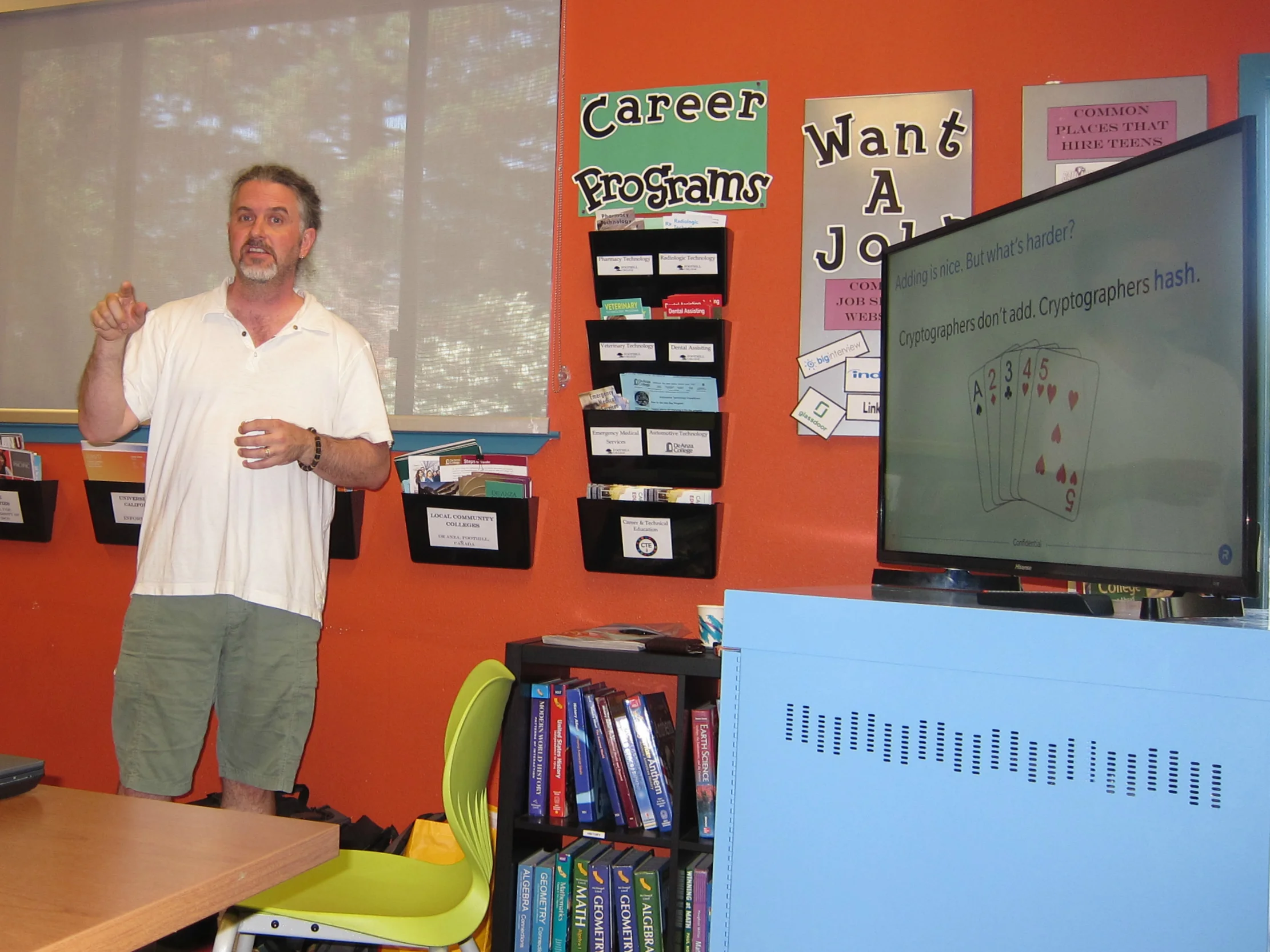
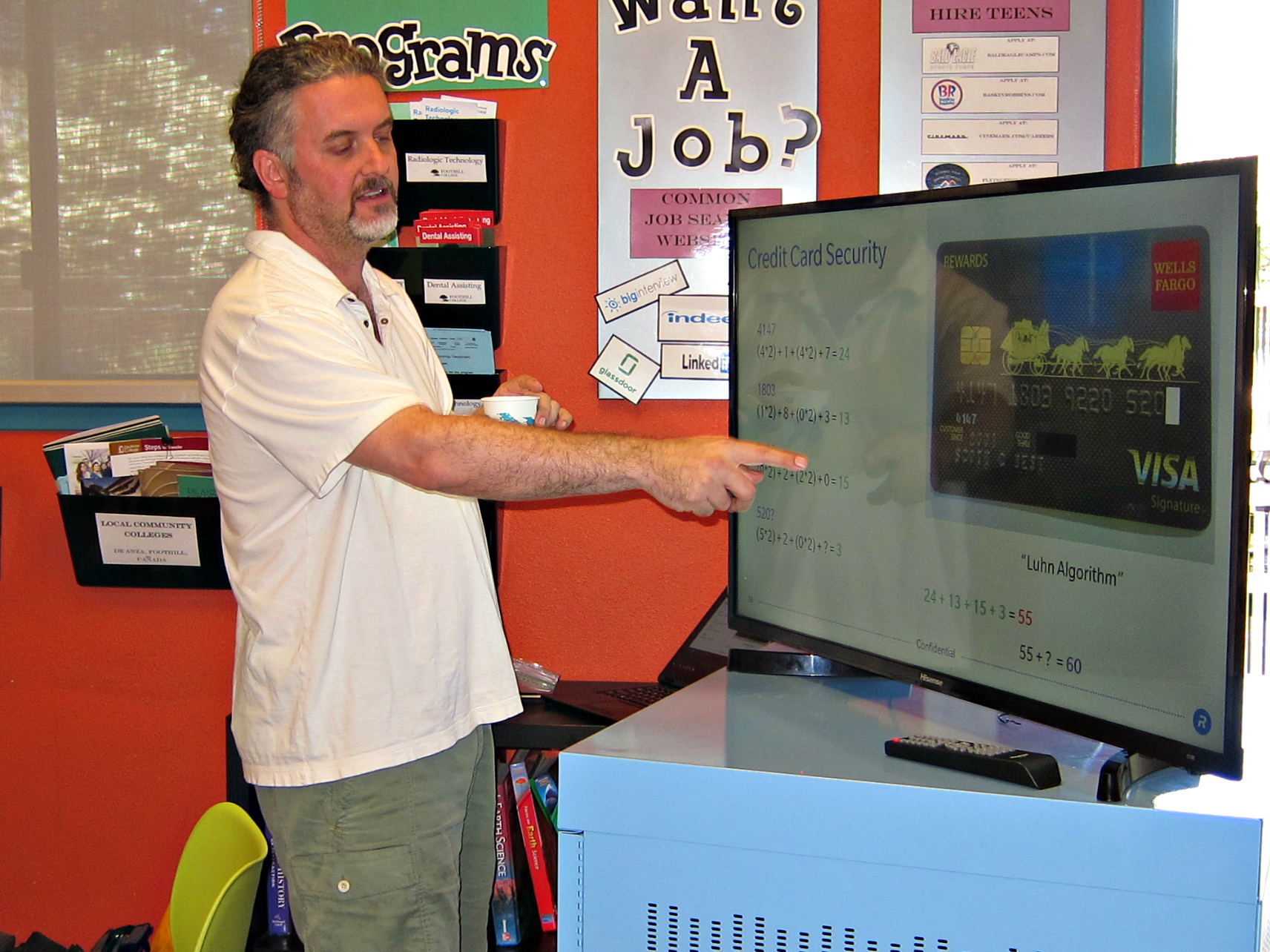
Best dives into the security of our credit cards; in addition to the magnetic stripes and the 16-digit code with a pattern (Luhn Algorithm), cards are now equipped with microchips that make them even more secure. However, even with all these layers of protection, credit cards can still be hacked. The magical code pattern for the digits of a credit card follows a simple addition algorithm, and other parts can still be replicated. Even if the chance may seem infinitesimal, there’s always a risk of a successful attack.
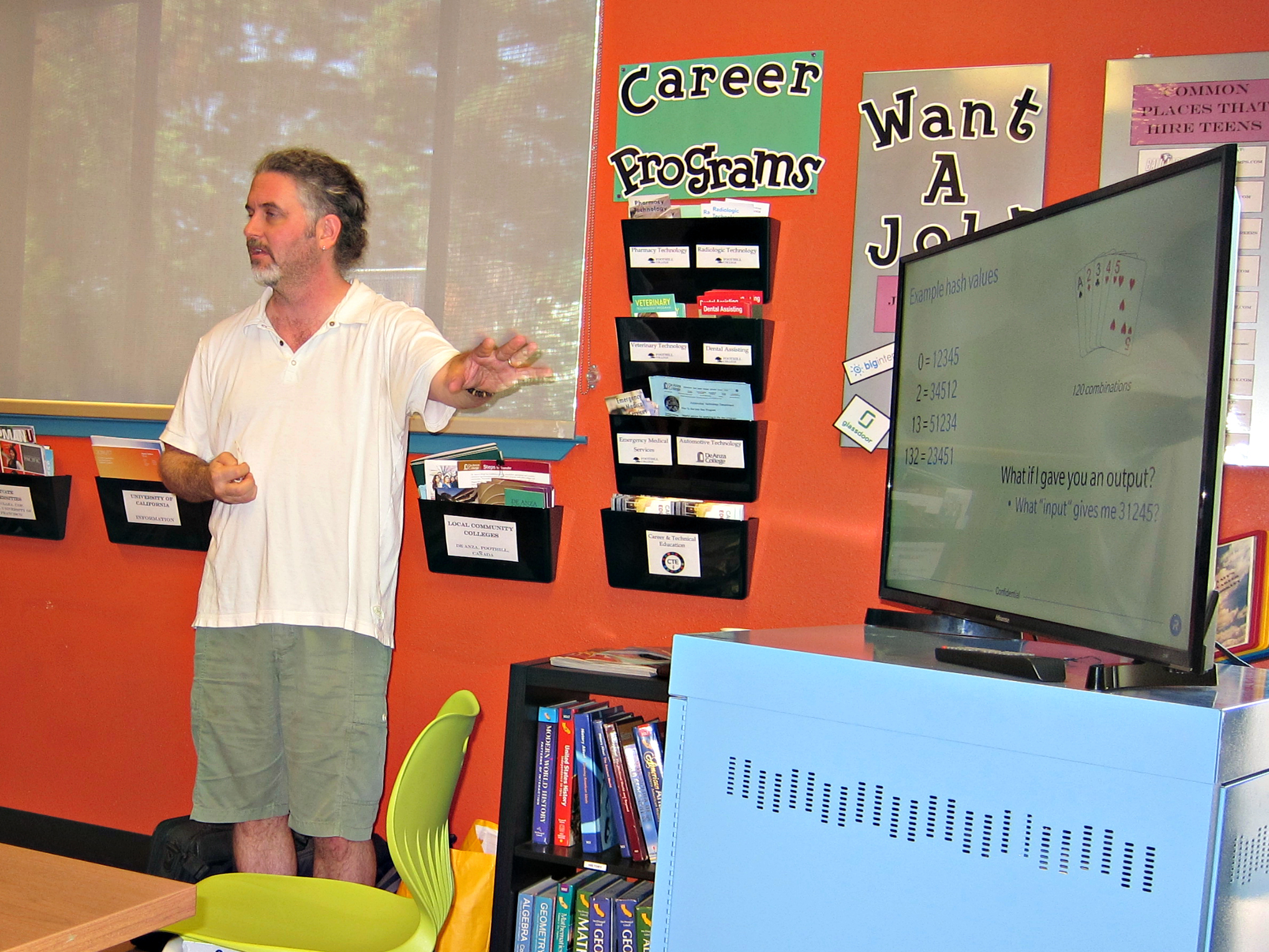
In contrary to using addition as a form of security, cryptographers like Best perform what is known as "hashing." In his presentation, Best uses a deck of playing cards to simulate the process of hashing, using random numbers to perform a set amount of operations on the cards, thus generating a final position. When trying to guess the initial number with a final position, however, he demonstrates that it is nearly impossible. Best shows that hashing is “very easy in one direction… and almost impossible in the other”, and explains that while many of the elite cryptographers have tried to break the code, the only method available right now is to guess and check, making it nearly impossible to hack.
**Bitcoin**
Finally, Best covers the big topic: the bitcoin. To many, the term is new or foggy - and it should be. After all, it was launched as a currency in 2009, and has only continued to expand each year. The bitcoin is a form of currency, just like gold or paper money, that can be spent or saved online. To understand the bitcoin, we must also understand the blockchain. The blockchain is essentially a ledger, a group of transactions displayed in a list, and a bitcoin is an entry on that ledger.
What makes the bitcoin so great? For starters, it is much more secure than cash; by using hashing and 256 digit codes, bitcoin is as secure as it gets. Not only that, but it is also more trackable and less anonymous than cash, making it less susceptible to hacking attempts. With the rapidly developing technology today, it’s no surprise that bitcoin continues to grow; transactions and storage are all managed by the speedy and efficient system known as the internet. In addition, bitcoin can only be shut down in one way - by turning off the internet, which certainly won’t be happening anytime soon.
In retrospect, the bitcoin shares many similar features with gold. Both serve as valid forms of money, and each are finite in value; there is only a limited value of gold on the planet, and there are only so many bitcoins floating around (after all, the amount is controlled). Unlike money, which suffers from constant production, both of these forms of money manage to retain its value and fight off inflation. And finally, gold is extremely valuable to us, and in the same way, so are bitcoins: one bitcoin holds the value of approximately 4,000 US dollars today!!!











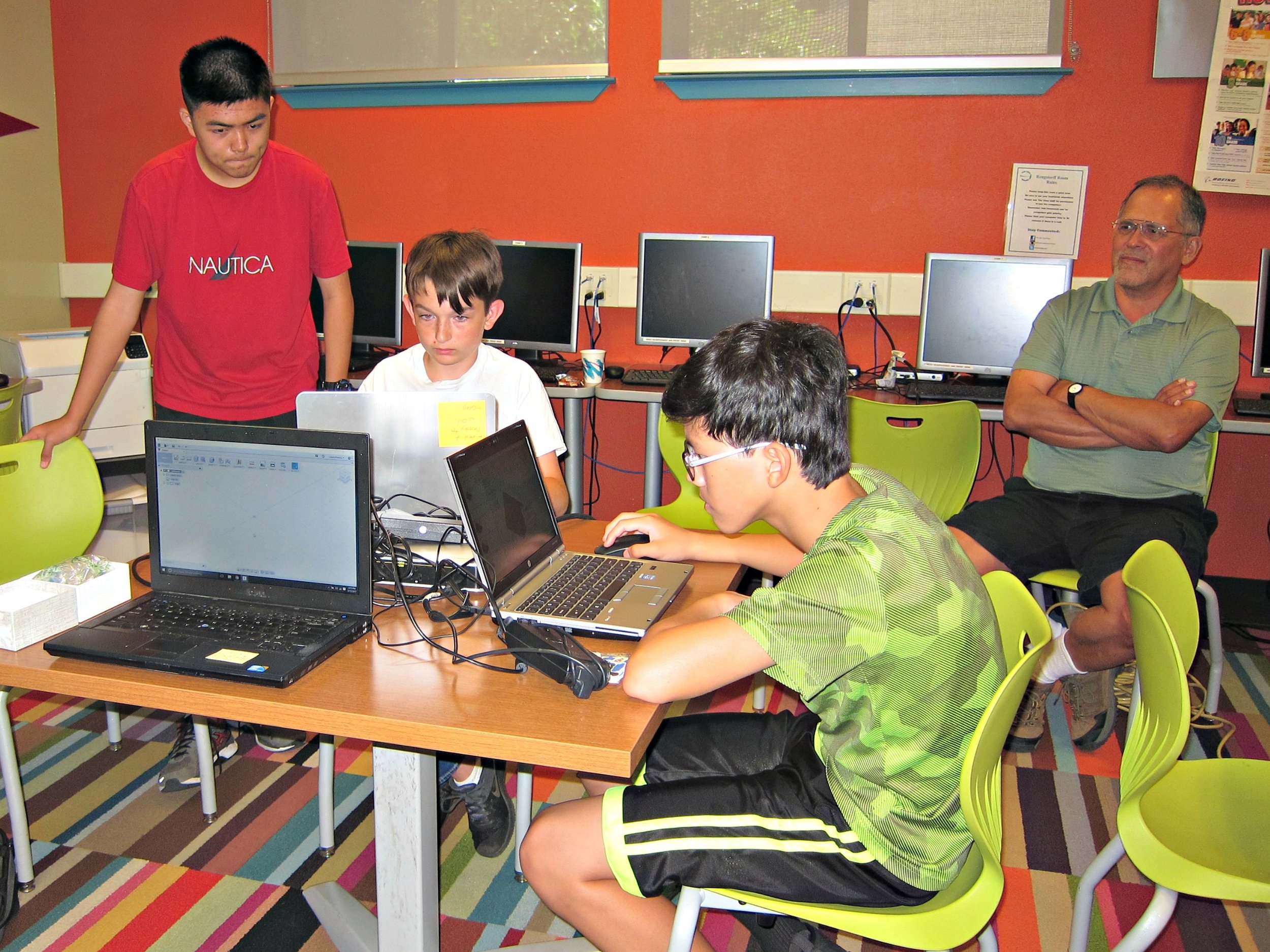
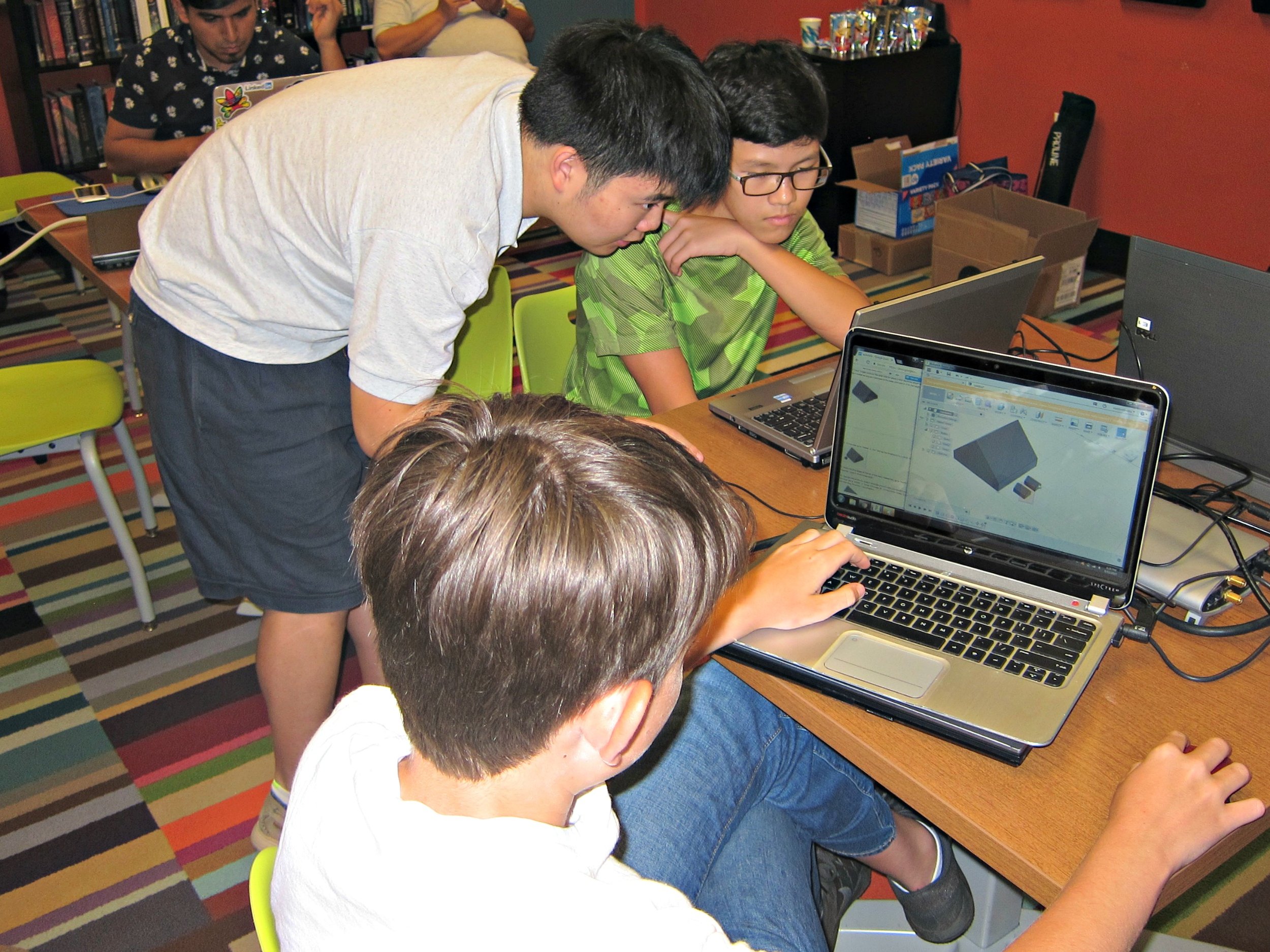
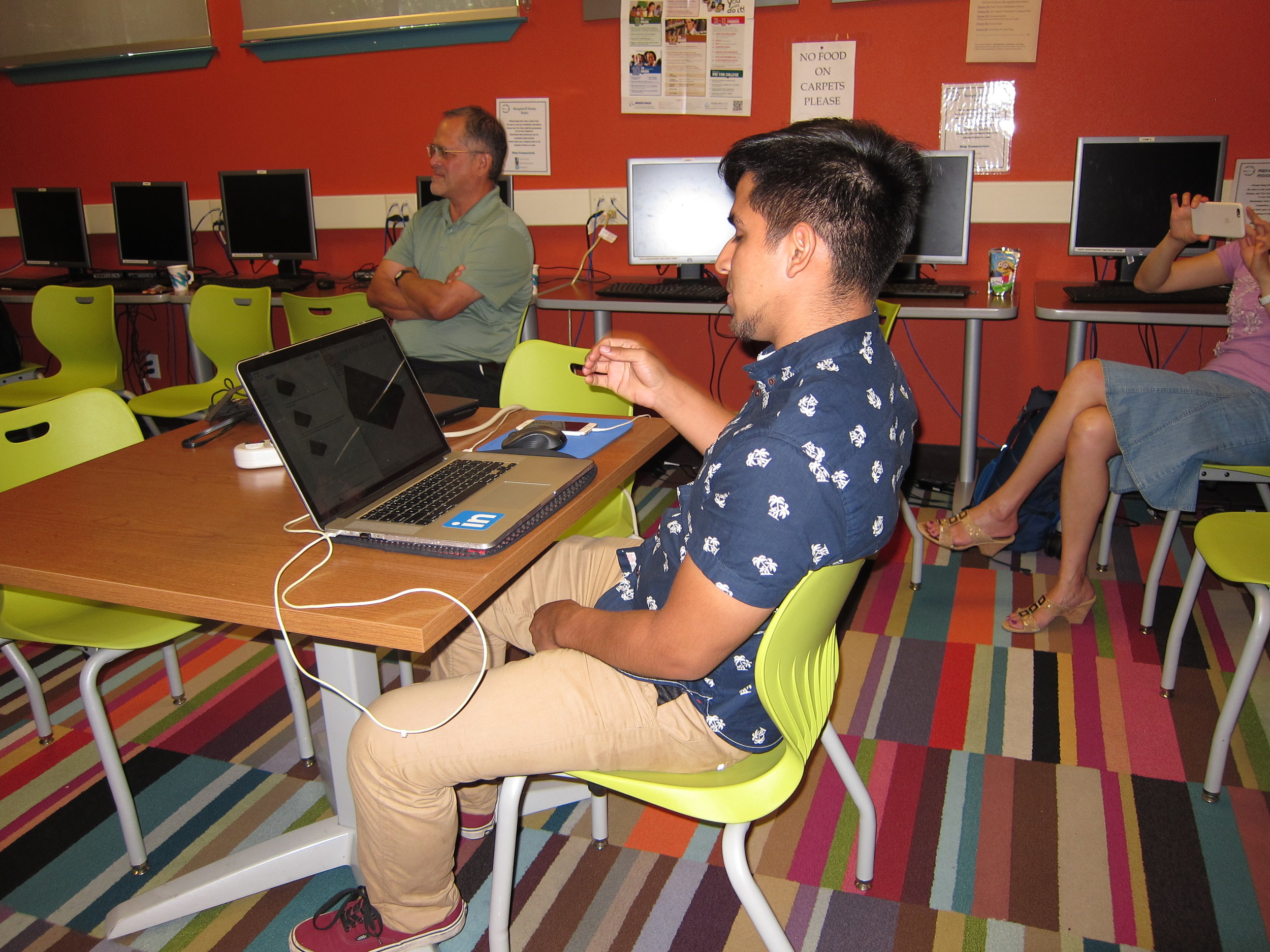
**Autodesk Fusion 360 CAD Design Workshop - led by Kevin Gao & Terence Lee**
Last week, students follow instructions to download Autodesk Fusion 360 and learn how to design a fidget spinner. In this week’s workshop, attendees use Fusion 360 to design more complex and advanced designs. Following the big TV screen and live instructions on their laptops, attendees are now able to build and design their own 3D houses and get a better feel for what CAD can do.
If you miss the Computer-aided Design workshops and wish to learn, access the following PDF documents to download Autodesk Fusion 360 and visit the tutorial for the fidget spinner and house design projects. Enjoy and have lots of fun.
EqOpTech would like to sincerely thank Mr. Best for taking the time to present an intriguing and golden presentation.




Access here for the presentation slide deck:
Our Equal Opportunity Technology program is made possible thanks to Los Altos Community Foundation community grant award.
Visit here for more information.












